
|
Friday, February 6, 2009 Y 7:01 PM Mechanisms involved in Anaphylaxis Anaphylaxis occurs when immunoglobulin E (IgE), which is produced by the body, reacts to protein which derived from our food or to certain type of drug. IgE stick to the cells in the body that release substances which affect blood vessels and air passages. The presence of the protein on the IgE on the cells leads to the release of these substances which in turn relaxes the blood vessels. These blood vessels become leaky and swell, lowering the blood pressure. In addition, breathing passages get narrowed. Anaphylaxis can be triggered by a particular allergen, mainly from food, medicine, insect sting, latex and even unknown cause. Exercising can cause exercise-induced anaphylaxis. Food Food allergy is a very common case of anaphylaxis. Research has showed that out of 5.4 to 7 million Americans who have food allergies, about 3 million are allergic to nuts alone. Food allergy has become an increasing concern that can result in around 125 deaths annually in United States. A simplified definition of food allergy means that when a person’s immune system reacts to food protein, which acts as a dangerous foreign substance, it will strengthen the body by developing IgE antibodies. Medicine Allergic reactions to medications can also cause anaphylaxis. Such allergens include penicilin, sulfa antibiotics, allopurinol and muscle relaxants. Most deaths from fatal anaphylaxis in the US are known to be caused by penicillin. Insect Sting Insects stings can trigger allergic reactions. Such insects include bees, wasps, hornets, yellow jackets and ants. When a person is bitten or stung by these insects, there can be two reactions; a normal response and anaphylaxis. A normal response can involve swelling, redness and pain at or around the site of the sting. Anaphylaxis could result from swelling of the throat or tongue, breathing difficulties, dizziness, severe headache, nausea, stomach cramp, diarrhea, rapid fall in blood pressure, shock, and also loss of consciousness. These symptoms should be noted as it could lead to deadly anaphylaxis within 1 to 2 minutes. Latex Latex allergy occurs when there is a systemic allergic sensitivity to the proteins present in natural rubber latex(NRL). Once there is exposure to NRL, subsequent exposures would worsen this sensitivity. Examples of materials that contain latex are car tires, rubber bands, carpet backing, hospital/dental equipment and more commonly latex gloves, balloons and condoms. Severe cases can cause death. Idiopathic Anaphylaxis A type of anaphylaxis which is triggered by unknown cause. Exercise – Induced Anaphylaxis Exercise – Induced Anaphylaxis is a physical allergy. The studies of this allergy are still on research. However, it has been found that certain medications such as aspirin or food taken before sports will increase the percentage of getting exercise – induced anaphylaxis. Individuals at risk are those with personal history or family atopy1. 1Atopy is the increased tendency seen in some individuals to produce IgE antibodies to innocuous substances. There are 2 major groups in the causes of anaphylaxis. IgE mediatied IgE will then stick to the cells, such as mast cells and basophils, so that they can be prepared to react when the allergen (food protein) is reintroduced. Once the exposure occurs, the mast cells will release mediators which includes histamine, leukotriene C4, prostaglandin D2 and tryptase in the tissues around the cells. This reaction causes the immediate onset of elevated secretion of mucus from mucous membranes, increased swelling of bronchial smooth muscle and a decrease in blood pressure. Also, making the breathing passage to decrease its width. Non-IgE mediated (“anaphylactoid” reactions) This reaction does not need an IgE immune reaction. It is usually caused by immediate exposure of mast cells and basophils. The same mediations are then released, producing the same effects. A simplified diagram of IgE mediated reaction 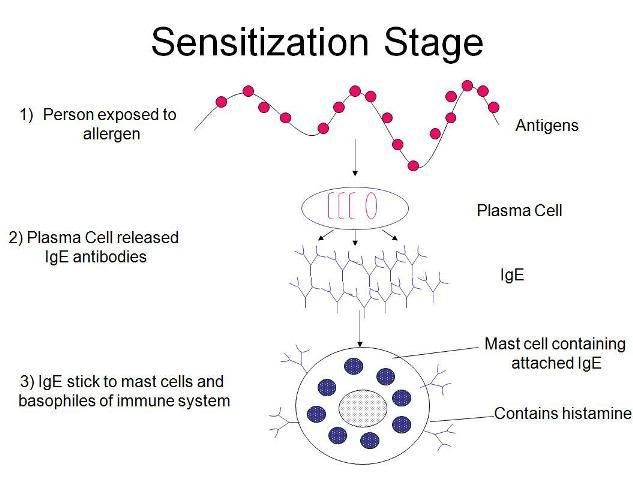 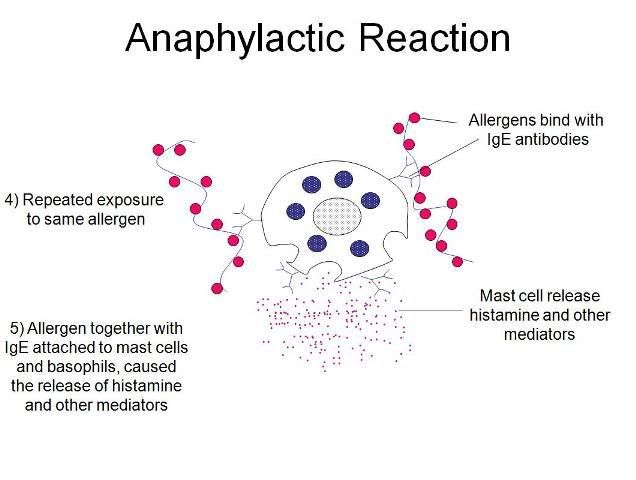 In conclusion, anaphylaxis is for reactions which are stimulated by IgE and anaphylactoid is for reactions which are not stimulated by IgE. However, the effects and treatments are the same. |
About Us  Sharna
Sharna Jocelyn 
Tasniyyah  Elizabeth
Elizabeth Poh Li
Poh Li Ying Hui
Ying HuiComments From Temasek Polytechnic Applied Food Science & Nutrition February 2009 Love in the Ice - 東方神起 thanks basecodes by: detonatedlove/♥s} images: deviantart designer: ٩͡๏̯͡๏)۶ |